What are Prototype Boards?
Prototype boards, also known as breadboards or protoboards, are essential tools for electronic designers and hobbyists alike. These boards provide a convenient and flexible way to create temporary circuits for testing and experimenting with various electronic components without the need for soldering. Prototype boards allow users to quickly assemble, modify, and disassemble circuits, making them ideal for developing and refining electronic designs before committing to a more permanent solution.
Types of Prototype Boards
There are several types of prototype boards available, each with its own unique features and benefits. Some of the most common types include:
- Solderless Breadboards
- Stripboards (Veroboards)
- Perfboards
- PCB Prototype Boards
Solderless Breadboards
Solderless breadboards are the most popular type of prototype board due to their ease of use and versatility. These boards feature a grid of holes connected by metal clips underneath, allowing components to be inserted and connected without the need for soldering. Breadboards typically have power rails running along the sides, providing convenient access to power and ground connections.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Holes | Arranged in a grid pattern, allowing components to be inserted |
| Connections | Metal clips underneath the board connect the holes |
| Power Rails | Strips running along the sides for power and ground connections |
| Ease of Use | Components can be quickly inserted, removed, and rearranged |
Stripboards (Veroboards)
Stripboards, also known as Veroboards, are prototype boards that feature a grid of holes with copper strips running along one side of the board. These strips allow for easy soldering of components and provide electrical connections between them. To create custom circuits, users can cut the copper strips as needed using a spot face cutter or drill.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Holes | Arranged in a grid pattern for inserting components |
| Copper Strips | Running along one side of the board for soldering and electrical connections |
| Customization | Strips can be cut to create custom circuits |
| Permanence | Soldered connections provide a more permanent solution compared to breadboards |
Perfboards
Perfboards are similar to stripboards but lack the copper strips. Instead, these boards feature a grid of holes with no pre-defined electrical connections. Users can create their own connections by soldering components and wires together as needed. Perfboards offer greater flexibility in circuit design but require more effort to create connections compared to stripboards.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Holes | Arranged in a grid pattern for inserting components |
| No Pre-defined Connections | Users create their own connections by soldering |
| Flexibility | Allows for complete customization of circuit layout |
| Effort | Requires more time and effort to create connections compared to stripboards |
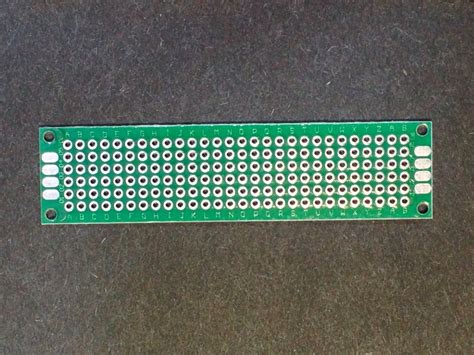
PCB Prototype Boards
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) prototype boards are custom-designed boards that closely resemble the final product. These boards are manufactured using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software and feature pre-defined copper traces, component footprints, and silkscreen labels. PCB prototype boards are ideal for testing and validating designs before mass production.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom Design | Created using CAD software to match the final product |
| Pre-defined Traces | Copper traces are printed on the board according to the design |
| Component Footprints | Specific areas for component placement |
| Silkscreen Labels | Text and symbols printed on the board for easy identification |
| Validation | Allows for testing and validation of designs before mass production |
Choosing the Right Prototype Board
When selecting a prototype board for your project, consider the following factors:
- Project Complexity
- Required Customization
- Permanence of Connections
- Budget and Time Constraints
For simple circuits and quick experimentation, solderless breadboards are often the best choice. They allow for rapid prototyping and easy modifications without the need for soldering.
If your project requires a more permanent solution but still needs some level of customization, stripboards or perfboards may be more suitable. These boards allow for soldered connections and custom circuit layouts, providing a more stable and durable prototype.
For projects that demand a high level of customization and resemble the final product, PCB prototype boards are the ideal choice. These boards offer the most professional and polished look, but they also come with a higher cost and longer lead times.
Working with Prototype Boards
Solderless Breadboards
When working with solderless breadboards, follow these tips for successful prototyping:
- Familiarize yourself with the breadboard layout and hole connections.
- Use jumper wires to create connections between components and power rails.
- Keep wire lengths as short as possible to minimize signal interference.
- Use color-coded wires to keep your circuit organized and easy to follow.
- Double-check your connections before applying power to the circuit.
Stripboards and Perfboards
When working with stripboards or perfboards, consider these guidelines:
- Plan your circuit layout before starting to solder components.
- Use a spot face cutter or drill to break copper strips on stripboards as needed.
- Apply heat shrink tubing or insulation tape to prevent short circuits.
- Use a soldering iron with a fine tip for precise soldering.
- Test your connections with a multimeter to ensure proper continuity.
PCB Prototype Boards
When designing and working with PCB prototype boards, keep these points in mind:
- Use CAD software to create your board design, including component footprints and copper traces.
- Follow the manufacturer’s design guidelines for minimum trace widths, spacing, and hole sizes.
- Consider using surface mount components to save space and improve performance.
- Include silkscreen labels for easy component identification and orientation.
- Test your prototype board thoroughly before proceeding with mass production.

Advantages of Using Prototype Boards
Using prototype boards offers several advantages in the electronic design process:
- Quick and Easy Circuit Creation: Prototype boards allow for rapid assembly and modification of circuits without the need for soldering.
- Cost-effective Experimentation: Prototype boards are relatively inexpensive, making them ideal for testing and refining designs before investing in more costly solutions.
- Flexibility and Customization: With various types of prototype boards available, designers can choose the best option for their specific needs and customize their circuits accordingly.
- Educational Value: Prototype boards are excellent tools for learning electronic principles and gaining hands-on experience with circuit design.
- Improved Design Validation: By testing and refining designs on prototype boards, designers can identify and resolve issues early in the development process, ultimately leading to a more successful final product.
Limitations of Prototype Boards
While prototype boards offer many benefits, they also have some limitations:
- Limited Durability: Solderless breadboards and other prototype boards are not designed for long-term use or harsh environments. The connections may become loose over time, leading to intermittent failures.
- Signal Integrity Issues: The long leads and interconnects on prototype boards can introduce signal integrity issues, particularly at high frequencies. This can cause problems with sensitive analog circuits or high-speed digital designs.
- Size Constraints: Prototype boards may be larger than the final PCB design, which can make it challenging to test the circuit in its intended form factor.
- Power Handling Limitations: Prototype boards may not be suitable for high-power applications due to the limited current handling capacity of the boards and the risk of overheating.
Conclusion
Electronic prototype boards are invaluable tools for designers and hobbyists working on electronic projects. They provide a flexible, cost-effective, and efficient way to create, test, and refine circuits before committing to a final design. By understanding the different types of prototype boards available and their respective advantages and limitations, users can select the best option for their specific needs and successfully bring their electronic ideas to life.
FAQ
- What is the difference between a solderless breadboard and a stripboard?
-
A solderless breadboard allows components to be inserted and connected without soldering, while a stripboard requires soldering components to the copper strips on the board.
-
Can I reuse a prototype board for multiple projects?
-
Yes, most prototype boards can be reused for multiple projects. However, solderless breadboards may lose their effectiveness over time due to wear on the metal clips.
-
How do I choose the right prototype board for my project?
-
Consider factors such as project complexity, required customization, permanence of connections, and budget when selecting a prototype board. Solderless breadboards are best for quick experimentation, while PCB prototype boards are ideal for more complex and permanent designs.
-
What tools do I need to work with prototype boards?
-
The tools required depend on the type of prototype board. For solderless breadboards, you’ll need jumper wires and a power supply. For stripboards and perfboards, you’ll need a soldering iron, solder, and a spot face cutter or drill. PCB prototype boards require CAD software for design and may need additional tools for assembly.
-
Can I use prototype boards for high-frequency or high-power applications?
- Prototype boards may not be suitable for high-frequency or high-power applications due to signal integrity issues and power handling limitations. In these cases, it’s best to use specialized PCBs designed for such applications.





Leave a Reply