Introduction
Printed circuit board (PCB) assembly is a complex process that involves soldering and assembling various electronic components onto a PCB. While some companies choose to handle PCB assembly in-house, many find it more efficient and cost-effective to outsource this process to a contract manufacturer.
PCB assembly contract manufacturers offer a range of benefits, including access to the latest equipment, technical expertise, flexibility, and the ability to scale production up or down as needed. This allows companies to focus their resources on design and other core competencies while leveraging the capabilities of an experienced partner.
This guide provides an in-depth look at PCB assembly contract manufacturing, including how the process works, key factors in choosing a provider, and the main benefits of outsourcing production.
Overview of the PCB Assembly Process
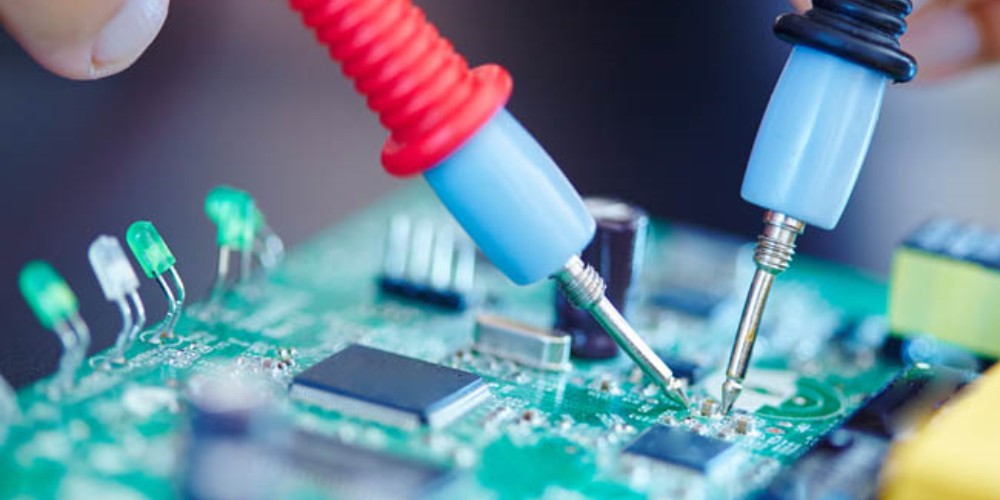
PCB assembly involves three main steps:
Solder Paste Application
The first step is applying solder paste to the PCB. This paste will form both the mechanical and electrical connections between components and the board during soldering. Solder paste is applied to pads and traces on the PCB using stencils and a printing process.
Component Placement
Next, electronic components must be precisely placed onto the PCB. This includes surface mount devices (SMD) such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits (ICs), as well as through-hole components with leads that go through holes in the PCB. Automated pick-and-place machines accurately position components in seconds.
Soldering
Finally, the board moves through a reflow oven that melts the solder paste to form permanent solder joints that adhere components to the PCB. For through-hole components, wave soldering makes connections by briefly submerging the underside of the board in a wave of liquid solder.
Additional processes like cleaning, inspection, and testing may take place before or after soldering to ensure quality and full functionality.
Choosing a PCB Assembly Contract Manufacturer
When selecting a contract manufacturer for PCB assembly, there are several key factors to consider:
Technical Capabilities
The company should have experience with the type of assembly required for your boards. This includes supporting fine-pitch components, BGAs, and other specialized assembly. They should also be able to work with various PCB materials, finishes, and board sizes.
Quality Processes
Look for robust quality control procedures like automated optical inspection (AOI), in-circuit testing, and end-of-line auditing. ISO certification and traceability are also signs of a focus on quality.
Turnaround Time
Choose a manufacturer that can meet your time-to-market requirements. Ask about typical lead times and on-time delivery rates. Local providers may offer quicker turnaround.
Location
Consider the location of the facility in terms of logistics, shipping costs, travel for engineering support, and time zone alignment.
Scalability
The company should be able to adjust capacity to meet changing production needs. Review equipment and space to support scaling up or down.
Pricing
Compare pricing models (per unit, tooling fees, etc.) and total costs. Get quotes for prototyping, low-volume, and higher-volume production.
Engineering Support
Look for design for manufacturing (DFM) services to help optimize boards for assembly. On-site engineering support is also beneficial.
Certifications
Relevant certifications like IPC membership demonstrate ongoing training and expertise in electronics manufacturing.
Proactive Communication
Choose a provider that provides consistent project updates and quickly responds to issues. Good communication reduces delays and ensures transparency.
By thoroughly evaluating PCB assembly contractors on these criteria, you can select a partner able to deliver high-quality boards on time and on budget.
Key Benefits of Outsourcing PCB Assembly

There are a number of compelling reasons to use a contract manufacturer for PCB assembly:
Access to Advanced Technology and Equipment
A dedicated provider continuously invests in new equipment like solder paste printers, pick-and-place machines, and AOIs. Working with the latest technology is crucial for assembling today’s small, dense PCBs.
Technical Expertise and Best Practices
Experienced assembly technicians and engineers bring specialized skills for process optimization, troubleshooting, and quality control. They also stay updated on the latest standards and best practices.
Improved Efficiency and Cost Savings
By leveraging an existing facility with trained staff, organizations minimize capital outlays and avoid the costs of training internal teams. Contract manufacturers also maximize throughput and economies of scale.
Flexible Scaling
The ability to quickly ramp production up or down makes it easier to respond to changing market demand. Companies avoid excessive fixed costs when sales are low.
Faster Time-to-Market
Parallel manufacturing allows a contract provider to assemble PCBs while a product is being designed, eliminating delays. Their expertise also avoids potential mistakes that could slow introduction.
Focus on Core Competencies
Rather than divert resources to manufacturing operations, companies can concentrate on product design, development, and other areas that drive innovation and revenue.
For most organizations, partnering with a knowledgeable PCB assembly contract manufacturer results in higher quality, better cost control, and faster time-to-market than attempting to manage production internally.
Selecting an Optimal PCB Layout
To maximize the benefits of outsourcing, it helps to optimize your PCB layouts for manufacturing. Here are some key design considerations:
Component Placement
Strategically group and orient components to minimize pick-and-place machine movement. Follow assembly order from one side or corner.
Board Size and Panelization
Standardize on common board sizes and panel dimensions where possible. This allows for easier fixturing and processing.
Fine-Pitch Parts
Allow extra spacing around fine-pitch BGAs, QFNs, 0201s and other microcomponents for improved yield and inspectability.
Thermal Relief
Use thermal pads and sufficient copper to prevent solder cracking on high-power components. This improves reliability.
Test Points
Include testpoints to simplify in-circuit testing. Test pads should be accessible by probes and optimized for contacting.
Board Finish
A lead-free HASL, immersion silver, or OSP finish offers the best solderability and consistency. Avoid ENIG with nickel due to black pad risk.
By designing for assembly and manufacturing, you can maximize quality and throughput in PCB assembly. Your contract manufacturer can provide detailed DFM guidelines.
FQA
What are the main steps in PCB assembly?
The main steps in PCB assembly are:
- Solder paste application – Solder paste is printed on the PCB using stencils to form solder deposits.
- Component placement – Surface mount and through-hole components are accurately positioned onto the PCB.
- Soldering – The PCB passes through a reflow oven to securely attach components.
- Testing and inspection – Quality checks like AOI and ICT ensure boards function properly.
What is the most important factor when choosing a contract manufacturer?
The most important factors are technical capabilities, quality control processes, certifications, location, and scalability. The contractor must have proven experience assembling PCBs using the required methods and technologies to meet quality and volume needs.
What are the biggest benefits of outsourcing PCB assembly?
The major benefits are reduced costs, faster time-to-market, quality improvement, flexible scaling, and being able to focus resources on core competencies rather than manufacturing operations.
How can PCB layout impact the assembly process?
Optimized PCB layouts facilitate assembly by allowing for efficient component placement sequences, adequate spacing and solder joints, standardized sizes, easier testability, and manufacturable finishes and features.
What steps ensure quality in PCB assembly?
Key quality steps include solder paste inspection, automated optical inspection after soldering, in-circuit testing, end-of-line auditing, traceability through serialization and version control, environmental conditioning, and robust process controls at each stage.






Leave a Reply