Introduction to PCBs
A printed circuit board (PCB) is an essential component of most modern electronics. It provides the physical foundation on which microchips, capacitors, resistors and other electronic components are mounted. PCBs allow different components to be interconnected to create functional circuits and products.
PCBs have revolutionized electronics by enabling compact design and automated manufacturing. In this article, we will explore PCB technology in depth, focusing especially on boards made by the global electronics leader Panasonic.
What is a PCB?
A PCB consists of a flat, non-conductive board made from materials such as plastic or fiberglass. The board is coated with a layer of conductive copper, which is etched away to create a specific circuit pattern. Electronic components are soldered onto the copper traces to connect them together.
- Substrate – Forms the foundation. Usually fiberglass which offers rigidity and resistance to high temperatures. Can also be specialty materials for flexible PCBs.
- Conductive Layer – Usually a thin sheet of copper laminated onto the substrate. Etched to form traces and pads.
- Solder Mask – Coats the PCB except for exposed pads. Prevents solder bridging between copper traces.
- Silkscreen – Printed markings to identify components and connections.
- Finish – Coating such as tin or gold plating applied to exposed copper for protection and solderability.
Diagram of a typical PCB
PCBs provide a sturdy base for mounting small, delicate electronic components. The conductive copper traces interconnect components in a precise circuit arrangement. In essence, PCBs form the wiring and foundations for electronic devices.
Types of PCBs
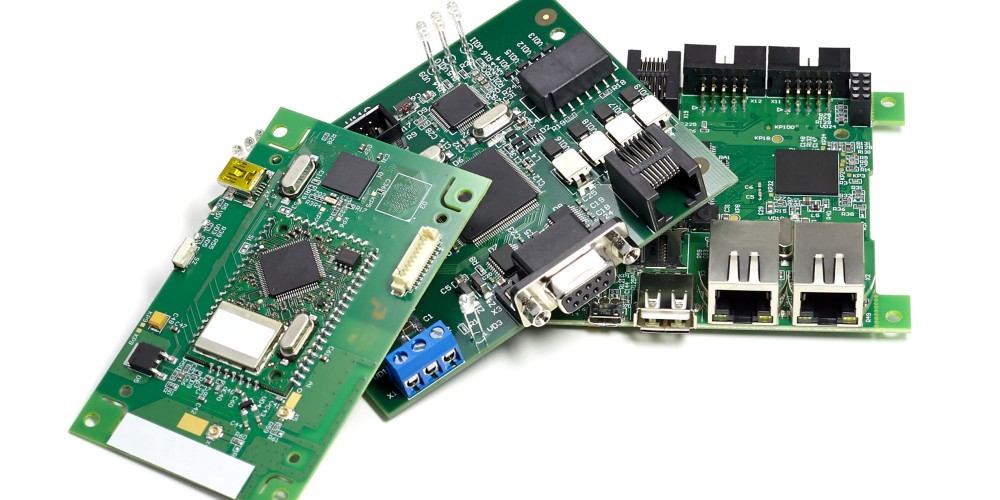
There are several types of PCBs designed for different electronic applications:
- Single-sided – Copper traces on one side only. Low cost but limited connectivity.
- Double-sided – Copper on both sides with plated through-holes to connect layers. Allows more complex circuits.
- Multilayer – Alternating layers of substrates and copper traces bonded together. Allows very complex, dense designs.
- Rigid PCB – Standard type using rigid fiberglass substrate. Most common variety.
- Flexible PCB – Uses flexible polymer substrates to interconnect electronics in bendable devices.
- Rigid-Flex PCB – Combines both rigid and flexible substrates for specialized applications.
- HDI PCB – High Density Interconnect with very dense component packing and trace routing. Used in advanced consumer electronics.
- Aluminum PCB – Metal substrate for improved thermal performance. Used in LED lighting and high power devices.
PCB Materials and Construction
Many types of materials are used in PCB fabrication to meet the demands of different electronics:
- Substrate materials: FR-4 Glass epoxy, CEM composites, Polyimide, PTFE, Aluminum
- Conductive layers: Copper, Silver, Aluminum
- Solder mask: LPI, Dry Film
- Finishes: HASL, Immersion Tin, Immersion Silver, ENIG, OSP
The substrate provides the PCB’s structural foundation. FR-4 fiberglass with an epoxy resin binder is the most common type – offering good strength, temperature resistance and dielectric properties. Copper foils form the conductive routing – with 1oz (35um) the standard thickness.
PCB manufacturing involves lamination, drilling, metallization, imaging, etching, stripping and finishing processes. Mass production uses sophisticated automation to precisely produce boards.
Benefits of Using PCBs
There are many benefits to constructing electronics circuits on printed circuit boards:
- Compact design – Allows placement of components close together and small product size.
- Efficient manufacturing – Automated PCB assembly lowers production costs.
- Reliability – Protects delicate components from vibration, moisture and contaminants.
- Serviceability – Easier to troubleshoot and repair compared to point-to-point wiring.
- Flexibility – Wide range of PCB types for specialized applications.
- Heat dissipation – FR-4 substrate helps conduct heat away from heat-generating components.
- High Speeds – Careful layout enables signals to propagate faster with less noise.
PCBs enable miniaturization, automation, reliability and performance – all crucial factors for modern electronics.
PCB Manufacturer – Panasonic
Panasonic is a large Japanese corporation and one of the world’s biggest PCB manufacturers. Founded in 1918, it produces a wide range of electronics products including home appliances, batteries, semiconductors, and automotive systems.
The company operates dozens of PCB and semiconductor fabrication plants across Asia and has an annual PCB production capacity exceeding 185 million ft2. It produces over 5000 different PCB types for products ranging from consumer devices to industrial equipment.
Some notable aspects of Panasonic PCB technology include:
- High-density multi-layer boards up to 24 layers.
- Fine line/space of under 8 micrometers.
- Excellent thermal management substrates.
- Flexible boards with bend radius down to 50 micrometers.
- High frequency boards over 65GHz.
- Halogen-free, low emission materials.
Panasonic PCBs are known for their high reliability and are widely used in the automotive, industrial, home appliance and consumer electronics sectors.
Panasonic PCB Products
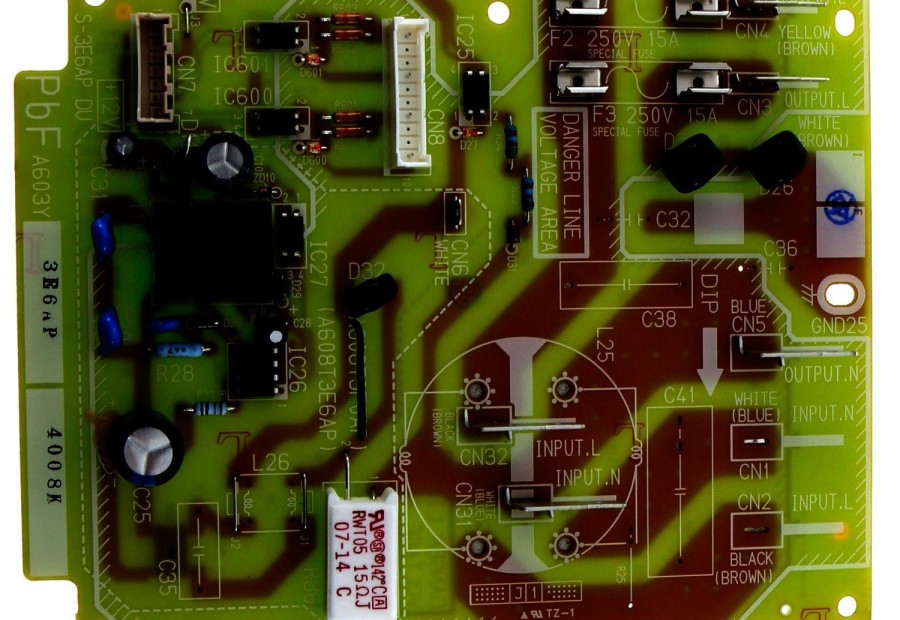
Panasonic offers of a wide selection of PCB products spanning multiple technologies:
Rigid PCBs
From cost-effective single layer boards to advanced multilayer HDI boards. Materials include FR-4, polyimide, halogen-free.
High Thermal PCBs
Aluminum or ceramic-based boards to dissipate heat from high power components.
Flexible & Rigid-Flex PCBs
Flexible circuits to interconnect electronics subject to movement and vibration.
RF/High Frequency PCBs
Low loss materials specialized for radar, 5G, communications, and wireless charging up to 65GHz.
Backplanes
Thick multi-layer boards to connect PCBs in servers, telecom, industrial systems.
IC Substrates
Advanced substrate for mounting bare semiconductors in products like smartphones.
Automotive PCBs
Boards meeting stringent quality standards for use in vehicle electronics.
This wide selection enables customers to choose the optimum PCB technology for their application and specifications.
Quality Control and Testing
To ensure reliability of its PCB products, Panasonic employs extensive quality control programs and testing procedures:
- Statistical process control to monitor manufacturing processes.
- Automated optical inspection (AOI) examines bare boards for defects.
- Electrical testing checks continuity, resistance, leakage, impedance.
- Cross-sectioning and microsectioning analyzes board construction.
- Environmental stress screening for thermal and humidity endurance.
- Vibration and bend testing evaluates robustness.
- Sample reliability testing such as HAST, pressure cook, temperature cycling.
- ISO 9001 certification of factories.
Rigorous quality control allows Panasonic to guarantee PCB boards that function flawlessly in customer products.
Conclusion
PCBs provide the vital wiring foundation that enables sophisticated and compact modern electronics. Leading manufacturer Panasonic produces a broad range of PCB technologies to suit diverse applications – from consumer gadgets to automotive systems.
With continued advancement of semiconductors, electronics products rely on very high performance boards. Panasonic’s expertise in PCB materials, manufacturing and testing allows it to stay on the leading edge. For electronics designers, Panasonic PCBs provide a reliable platform to build next-generation devices upon.
FQA:<h3>Questions and Answers on Panasonic PCB Boards</h3>
Q: What types of materials are used to make PCBs?
A: The most common PCB substrate material is FR-4 fiberglass epoxy. Other materials used include ceramics, polyimide, PTFE, and metal cores like aluminum or copper. The conductive traces are usually copper but sometimes silver or aluminum.
Q: What are some key benefits of using a PCB?
A: PCBs allow for compact, automated circuit construction. They protect delicate components, dissipate heat, and enable high frequency operation. PCBs are very reliable and make troubleshooting easier versus point-to-point wiring.
Q: What kind of PCBs does Panasonic manufacture?
A: Panasonic manufactures all the major PCB types – single-sided, double-sided, multi-layer, HDI, flexible, rigid-flex, aluminum core, RF, etc. This wide range caters to diverse electronics applications.
Q: How does Panasonic ensure its PCB quality?
A: Panasonic utilizes statistical process control, extensive testing and inspection, ISO certified factories, and sample reliability testing like HAST and temperature cycling. This quality control guarantees high performance boards.
Q: Can Panasonic manufacture PCBs for high frequency applications?
A: Yes, Panasonic makes RF and microwave PCBs that operate up to 65GHz for applications like 5G, radar, and satellite communications using low-loss materials. The company is experienced in high frequency PCB technology.






Leave a Reply